STEP 2 Scoring methodology
In the previous article, we discussed the earn mechanism and its significance for the loyalty program. In this section, we will describe the models for collecting points. The models for collecting points in a loyalty program vary in complexity and flexibility. Selecting the appropriate model is crucial for attracting and retaining loyal customers.
Earning points mechanism in Synerise
In the Synerise platform, the earn mechanism is configurable in two models:
- Threshold-based model
- Point collection-based model
The differences between them relate to how the activity is recorded, the points awarded and the rewards. Please refer to the table below for a detailed breakdown of each model.
| Threshold-based model | Point collection-based model | |
|---|---|---|
| Assumptions | Simpler, less customers activities. | More options and rewards, frequent customers interactions. |
| Reward | The higher the tier, the better the rewards; smaller pool of rewards. |
Same conditions for everyone, points redeemable for free products or discounts. |
Threshold-based model
The scoring for thresholds is calculated in similar way to the points balance, though the rules are usually more simple. You can build it on any activity-based metric, but majority of solutions choose spendings or/and purchasing frequency.
What is a tiered scenario
Tiered scenarios are loyalty programs in which customers earn successive layers, or levels based on calculated scoring.
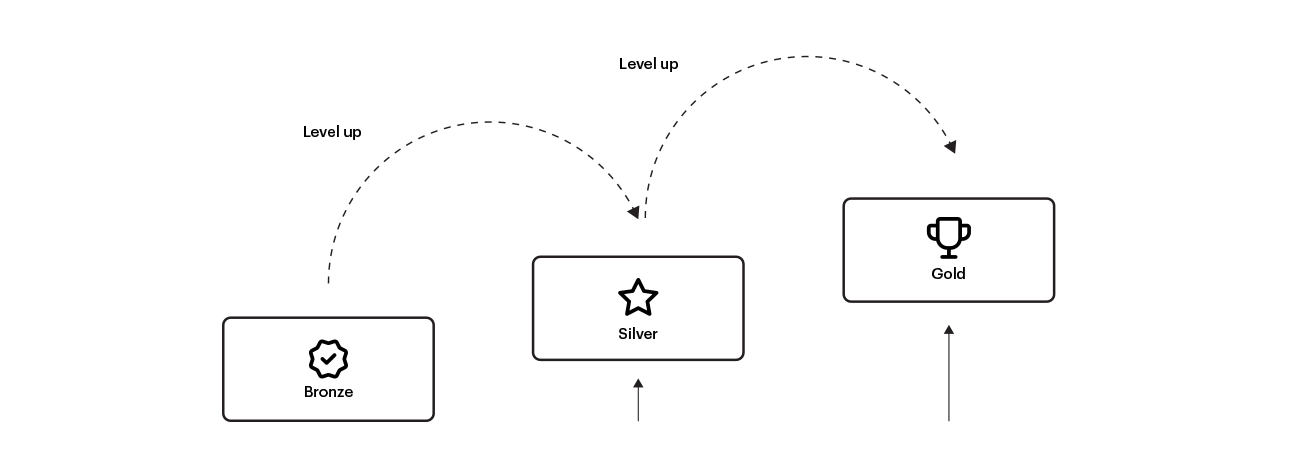
The loyalty model presented offers customers a graduated reward structure, which in turn encourages them to maintain engagement.
In tiered scenarios, each successive tier represents a higher level of loyalty and may be associated with more exclusive benefits, discounts or rewards. Advancement to a higher level may be dependent on achieving a certain number of points, purchase frequency, loyalty program activity or other specified criteria.
These types of loyalty programs aim to create a more dynamic and attractive experience for customers, who gain additional value each time they advance to a higher level. Tiered scenarios are becoming increasingly popular due to their effectiveness in shaping positive customer relationships and increasing customer engagement over the long term.
Tiers conditions types
Tiered scenarios can be built based on a variety of customer activities, both purchase-related and other customer activities. Some of the most popular include:
- Transactions value,
- Customer seniority,
- Customer activity (such as adding a review, playing a video, liking a page, and more),
- Frequency of purchases,
- Marketing consents.
The selection of factors to consider for layering is an individualized approach that should be considered as a customer engagement factor across multiple levels, not solely focused on the purchasing aspect.
In Tiered loyalty program use case customers will be assigned to one of the four levels (tiers) of the loyalty program based on the total balance value (transactions value minus the value of returns) from the last 365 days. Each tier is represented by a color.
Point collection-based model
Synerise offers two layers of schemes for building a point system.
- The basic points scheme
- Promotional points actions
The differences between the schemes relate to how points are accrued in loyalty programs. The precise distinction of each mechanism is described below.
The basic points scheme
The basic points scheme covers the fundamental rules for earning points, typically based on the amount spent but in general used for rules that are very rarely modified or do not change at all. This scoring model is effective when the program’s rules and stages are clearly defined.
USE CASES
We encourage you to check our use case Loyalty programs basics. In this use case, we will present a basic schema for building loyalty program, which is the necessary first step you have to make in the beginning if you wish to calculate points for purchased products. It might be treated as the basic loyalty program as a whole!
Promotional points actions
A promotional points-based scheme focuses on adding points for specific actions, customer activities. Examples of such activities that can be taken into account in the loyalty program are:
- Product page view,
- Buying a specific product, category or brand.,
- Newsletter subscription,
- After-sales survey submission.
Without any coding, based on the Synerise possibilities we can develop rules for calculating points for such activities.
This model is particularly dedicated to limited-time or exclusive offers.
USE CASES
Check an example configuration in Extra points for purchase from specific category during specific time. In this use case, purchase from the Christmas category during the pre-Christmas weekend are double-awarded.
Monitoring of points balance
A reminder of the points balance at each stage of the loyalty program is very important, so that we can avoid users getting stuck at one of the loyalty stages. Ongoing monitoring increases the efficiency of loyalty program by enabling any points-related issues to be resolved quickly. You can use API methods to display the points balance.
One common issue that companies encounter is customers failing to utilize their loyalty points. To address this, customers can receive an alert within the app reminding them of the upcoming expiration date of their points and the remaining time until they expire.
USE CASES
Read the In-app point balance reminder use case in which we show how to prepare an alert in a mobile app.
Next step
You already know how scoring works in Synerise, in the next article you will learn more about scenarios to put this knowledge into practice.