Dynamic content inserts
You can find the snippets in our Github repository: https://github.com/Synerise/jinja-code-snippet
Common tags available in dynamic content
You can use all tags from Insert usage.
Accessing meta properties
To access the value of a product: meta tag’s content attribute when creating dynamic content, use the following syntax:
{{ metric_additional_params["product:PARAM_NAME"] }}- This method only works with HTML meta tags that have the
propertyandcontentattributes. - This only works with
product:tags, for exampleproduct:retailer_part_no. It does not work with tags such asog:urland with theproduct:categorytag, which is reserved..
This allows you to modify and personalize the page depending on metadata. For example, you can manipulate search results or manipulate which catalogs are accessed.
Example
// Get the unique ID from meta tags:
{% set key = metric_additional_params['product:retailer_part_no'] %}
// Use the part number to retrieve the value of the 'title' column:
{% catalog.catalogName(key).title %}You can use this mechanism to retrieve data such as the name, price, or brand of an item from a catalog. Thanks to this, the catalog can become a single source of data for multiple websites that present the same item.
In this example, the insert is used in a dynamic content communication created for the article you are reading now.
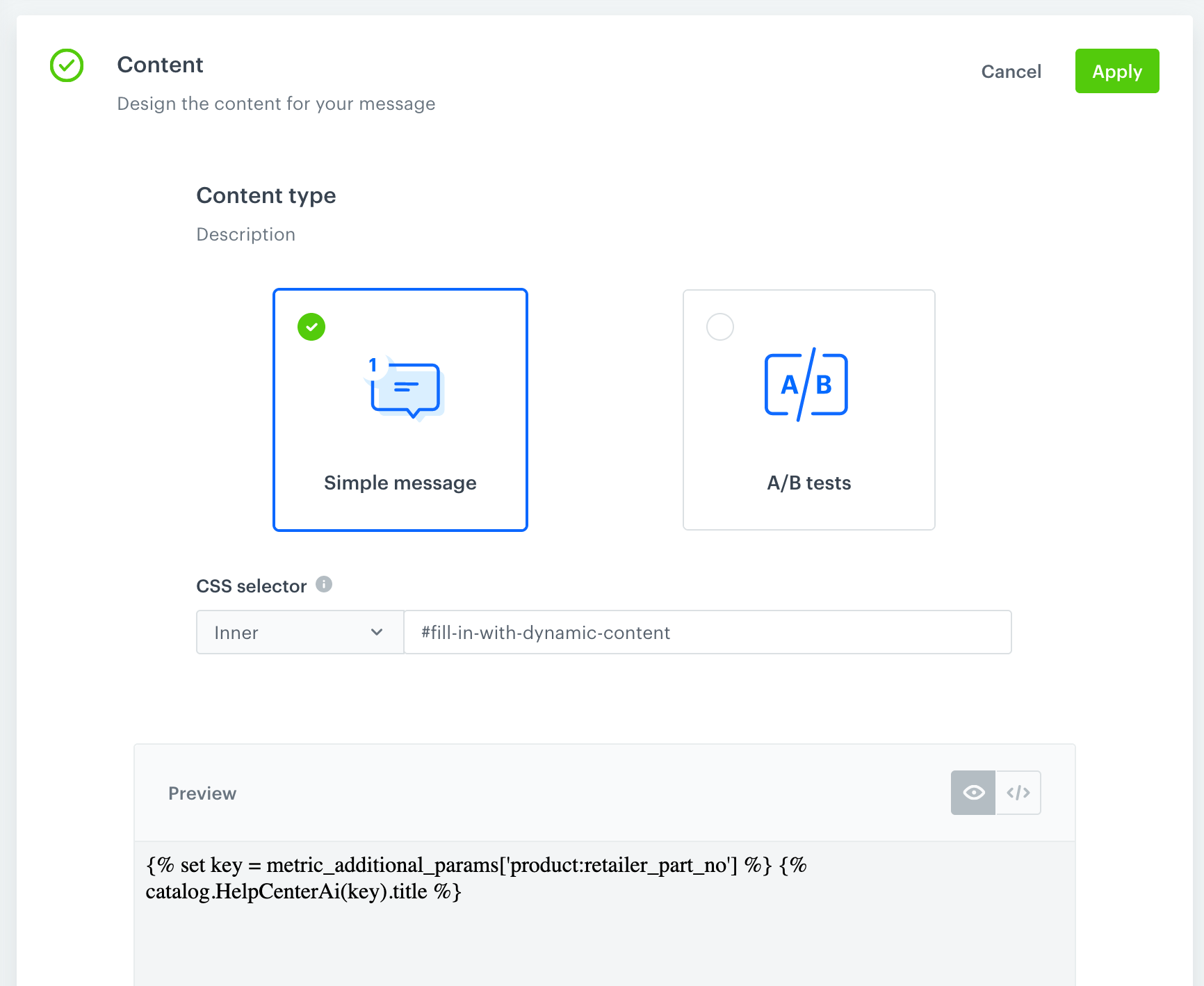
The communication:
- Checks the unique ID of the item (this article) in the page’s OG tags.
- Retrieves the title of the item from the
HelpCenterAicatalog in Synerise. - Replaces the content of the
codetag below with the retrieved title.
The content of the following code tag is replaced:
Replace this text
The original HTML code, before dynamic content is downloaded, is the following:
<code id="fill-in-with-dynamic-content">Replace this text</code>
Social proof
A social proof insert lets you retrieve a value of the metric.
- The metric must contain only one dynamic key.
- In the configuration of the metric, we recommend using the Equal operator instead of the Contain operator. The Contain operator in the social proof insert will work only if there is an exact match between the two compared elements (for example, when comparing
abctoabcd,abcwon’t be considered a match forabcd).
Syntax:
{% socialproof %} metric-hash {% endsocialproof %}Example:
The number of times the product was added to cart during the last 30 days.
<div class="snrs-wrapper">
<div id="snrsCornerMessage" class="snrs-corner-message-wrap">
<div class="snrs-corner-message">
<div class="snrs-corner-main">
<div class="snrs-corner-message-text">
This product has been added to the cart {% socialproof %} 537165da-9d8c-4460-a3a2-6294f1f7aef9 {% endsocialproof %} times in the last 30 days!
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Output (metric result is “235”):
<div class="snrs-wrapper">
<div id="snrsCornerMessage" class="snrs-corner-message-wrap">
<div class="snrs-corner-message">
<div class="snrs-corner-main">
<div class="snrs-corner-message-text">
This product has been added to the cart 235 times in the last 30 days!
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Validation
Whenever you use Jinjava in dynamic content, verify that it displays correctly for a few different test customers to make sure that the logic you applied covers all scenarios. If Jinjava fails to render, the communication is not sent to a customer at all.