Cart-Based Recommendation with Last Seen and Last Bought Exclusion
When building product recommendations in the checkout flow, it’s important to avoid redundancy and overexposure. Showing users items they’ve just viewed or recently bought can reduce relevance and lower conversion potential.
In this use case, we implement a recommendation that suggests products related to items currently in the cart. To ensure the results remain fresh and relevant, we apply the following filters:
- one to exclude last seen products,
- and another to exclude items recently purchased,
- using product context – excluding the currently viewed product from recommendations
- considering the product context – displaying recommendations from the same category as the currently viewed product.
Note: You can refine the item context even more by displaying items in the same color, style, or size as the item currently viewed, using the available item attributes in your product feed.
What is more, we will use boosting factors, to promote in recommendations products which:
- costs more than 10$. In this way, you exclude recommending products that are too cheap and encourage the purchase of more expensive ones.
This setup ensures that recommendations stay distinct from other modules on the page (like last seen or personalized offers) and avoid repeating content the user already interacted with — helping drive meaningful discovery and cross-sell opportunities. Additional boosting and filters let you present more personalized recommendations using the product context.
Prerequisites
- Implement a tracking code into your website.
- Configure AI engine. Enable similar item recommendation model.
- Implement the transaction events using SDK or API.
Process
In this use case, you will go through the following steps:
- Create an aggregate returning last seen products that returns the ID of the last seen product.
- Prepare an AI recommendation with the exclusion of last bought and last seen products.
Create an aggregate returning last seen products
In this part of the process, create an aggregate that returns the ID of the last 10 products a customer had visited. The recently viewed product itself will not display in the template, but will serve as a context for recommendations.
- Go to
 Behavioral Data Hub > Live Aggregates > Create aggregate.
Behavioral Data Hub > Live Aggregates > Create aggregate. - As the aggregate type, select Profile.
- Enter the name of the aggregate.
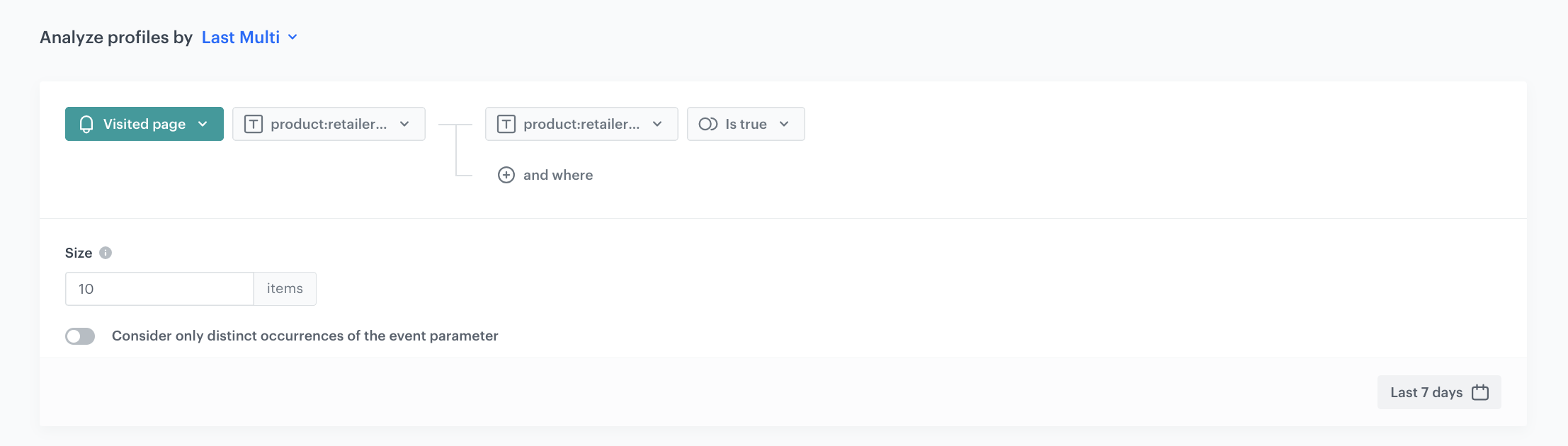
- Click Analyze profiles by and select Last Multi. As a size add 10. You can also add more results.
- From the Choose event dropdown list, select the Visited page event.
- As the event parameter, select product:retailer_part_no.
- Click the + where button.
- From the Choose parameter dropdown list, select the product:retailer_part_no parameter.
- From the Choose operator dropdown list, select Is true (Boolean).
- Using the date picker in the lower-right corner, set the time range to Last 7 days. Confirm your choice with the Apply button.
- Click Save.
Prepare an AI recommendation
In this part of the process, you will configure AI Recommendations which exclude last seen and last bought products. AI Recommendations will be added to the website to the product page.
-
Go to
 AI Hub > (AI Recommendations) Models > Add recommendation.
AI Hub > (AI Recommendations) Models > Add recommendation. -
Enter the name of the recommendation (it is only visible on the list of recommendations).
-
In the Type & Items Feed section, click Define.
-
From the Items Feed dropdown list, select an item feed.
-
In the Type section, choose the Similar items recommendation type.
-
Confirm the settings by clicking Apply.
-
In the Items section, click Define. 2. Define the minimum and maximum number of items that will be recommended to the customer in each slot. 3. Define Static filters and Elastic filters. 4. In our case, in the Elastic filter section, click Define filter.
5. Select Visual Builder.
6. Click Select value. 5. Choose itemId. 6. As an operator, choose Not in. 7. Click the icon which appeared next to the field with operator and from the dropdown list, select Aggregate. 8. From the list, choose the aggregate created in the previous part of the process. 4. Confirm by clicking Apply.<figure> <img src="/use-cases/all-cases/_gfx/elastic.png" alt="The view of the aggregate configuration" class="large"> <figcaption>Configuration of the elastic filter</figcaption> </figure>-
In the Static filters section, click Define filter.
-
Select Visual Builder.
-
From the Select value dropdown list, choose category.
-
As an operator, choose Equals.
-
Click the icon which appeared next to the field with operator and from the dropdown list select Context (eye icon).
-
From the Select value dropdown list, choose the category. Then, choose how you want to select your category level. In our case it will be Whole.
-
Click and where to add another filter.
-
From the Select value dropdown list, choose itemId.
-
As an operator, choose Does not equal.
-
Click the icon which appeared next to the field with operator and from the dropdown list, select Context (eye icon).
-
From the Select value dropdown list, choose itemID.
-
Confirm by clicking Apply.
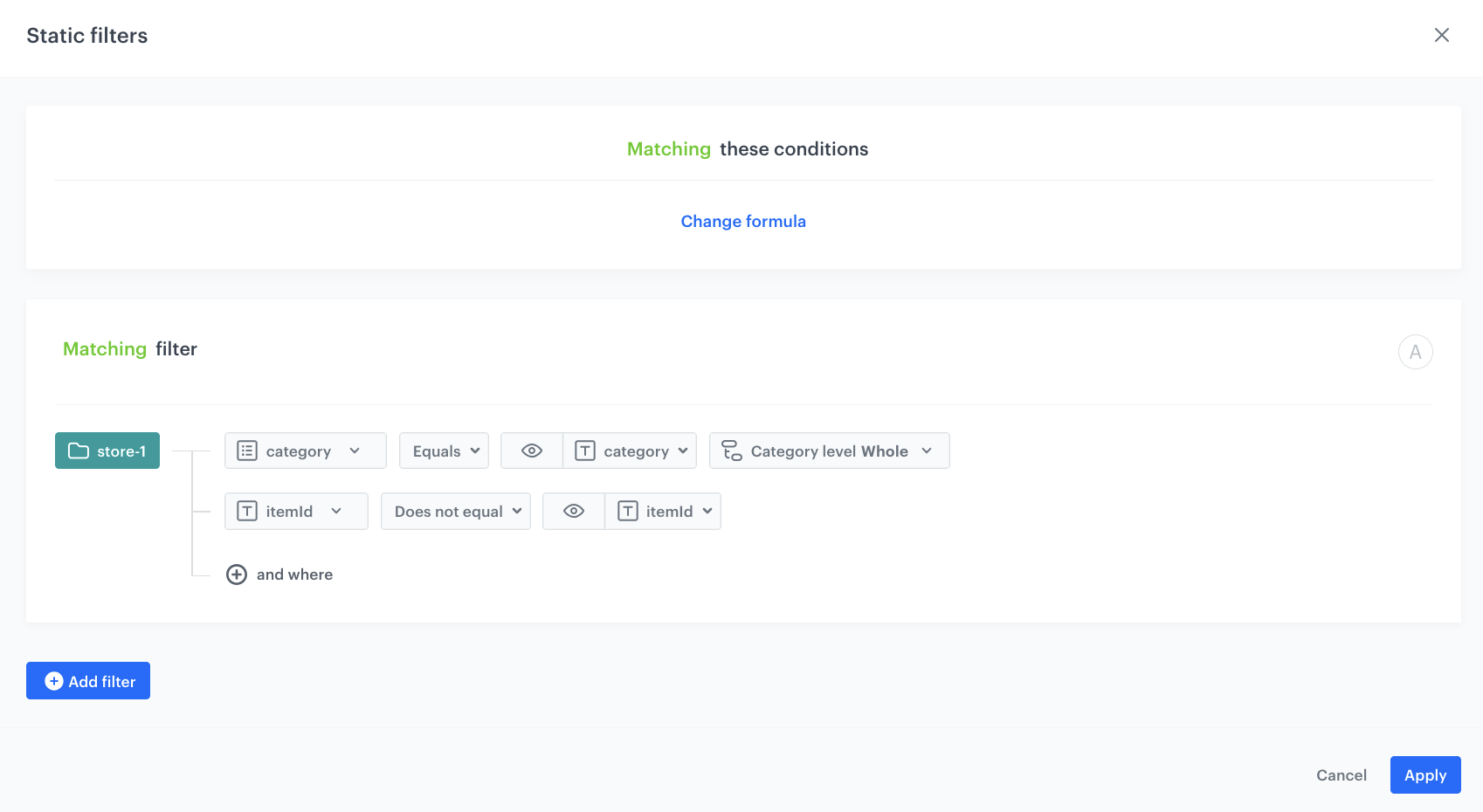
Configuration of the static filter
Note: You can refine the item context even more by displaying items in the same color, style, or size as the item currently viewed, using the available item attributes in your product feed. -
-
Define the boosting rules by clicking Define in the Boosting section.
- In Attributes section, click Add rule.
- Click Define rule.
- Choose Visual builder.
- From the Select value dropdown list, choose price.
- As Operator, choose More than.
- As the value, enter the minimum price a product should cost to be included in the recommendations. This way, you exclude recommending products that are too cheap and encourage the purchase of more expensive ones.
- Click Apply.
- Click Promote.
- In the Impact section, set the impact of this rule to High.
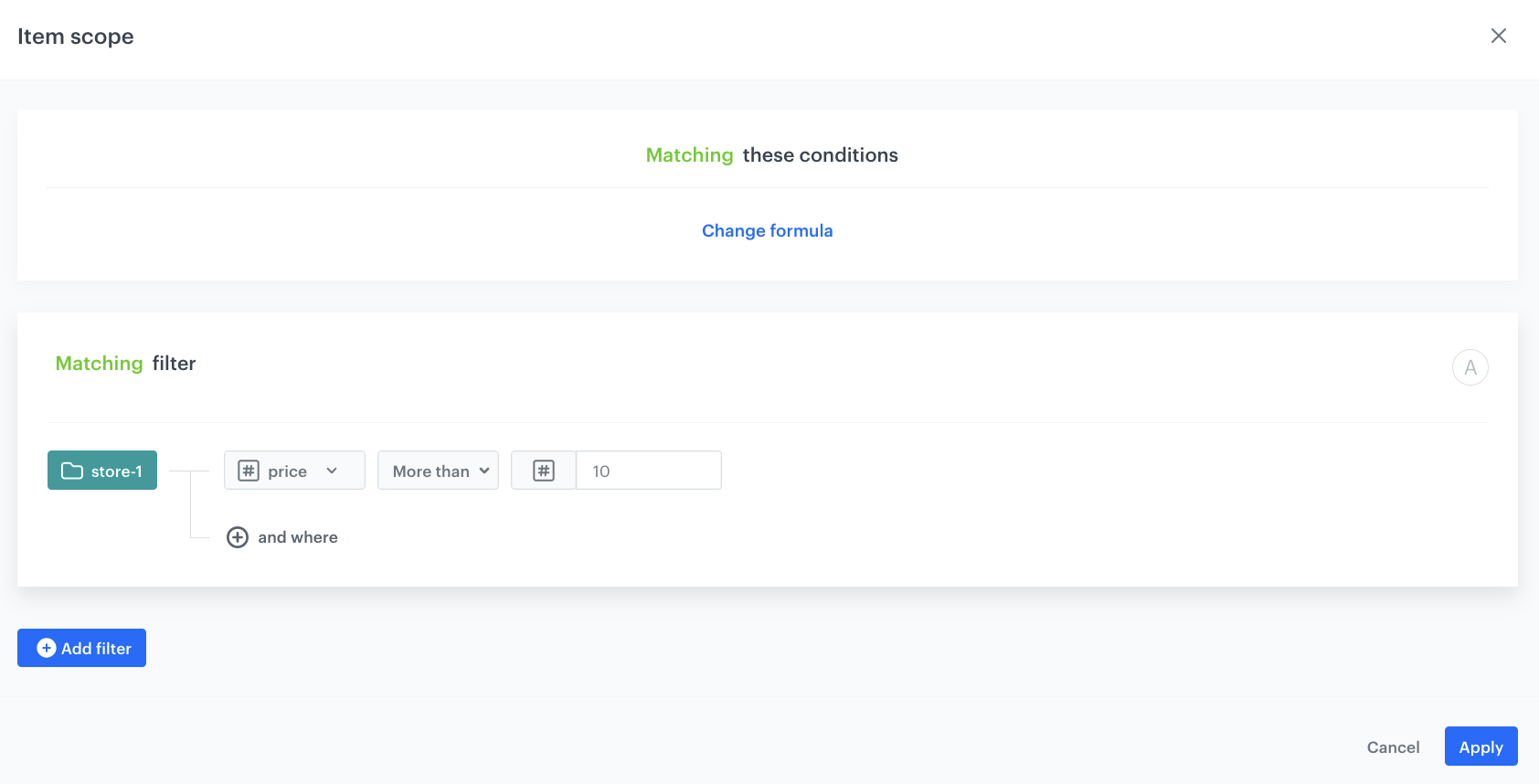
Configuration of the aggregate -
In the Additional settings section:
- Choose Exclude already bought products. If your company sells replenishable products, you can set exclusion for specific number of days, for example, exclude products bought not later than 30 days ago.
- To make sure that you only display available products in the recommendations, click Apply default filters.
-
In the right upper corner, click Save.
Check the use case set up on the Synerise Demo workspace
You can check the configuration of each step directly in our Synerise Demo workspace:
If you’re our partner or client, you already have automatic access to the Synerise Demo workspace (1590), where you can explore all the configured elements of this use case and copy them to your workspace.
If you’re not a partner or client yet, we encourage you to fill out the contact form to schedule a meeting with our representatives. They’ll be happy to show you how our demo works and discuss how you can apply this use case in your business.