Creating an external source
Instead of copying and updating data from various places, external sources let you get up-to-date information directly from external systems—like ERP, CRM, inventory, pricing, e-commerce platforms, other CMSs, or any REST API—and pull live data in real time when content is generated.
By creating an external source, you establish a connection with an external service by providing key details such as the endpoint URL, HTTP method (GET or POST), authentication method (API key, login/password, or SHA256-based), and other settings. During content generation—when an object with a record is generated or a record is previewed for the context of a specific profile in the editor—Synerise sends a request to the configured endpoint.
In the configuration of the external source, you can also use Jinjava (for example, in the endpoint URL or request body) to dynamically pass profile information in the request. At the end of the external source configuration, a preview cURL command is provided, which you can copy and test in your terminal or API testing tool.
This integration lets external data appear seamlessly as part of your content, just like data stored directly inside Brickworks. External sources eliminate multi-system integration complexity while ensuring your content remains accurate, complete, and contextually relevant—making it a live reflection of your entire business ecosystem.
Benefits
- Content always reflects the latest state of your business systems. Inventory counts, pricing, customer data, and metrics are fetched live when content is requested.
- Your applications make one API call to Brickworks and receive complete, enriched content that combines your managed content with live external data.
- No ETL jobs to monitor, no data synchronization to manage, no stale data concerns. External systems remain the single source of truth.
- External sources can use context parameters and other record’s simple fields to fetch precisely the right data for each request, enabling dynamic, personalized content experiences.
Example use cases
You can use external sources in the following cases:
- E-commerce operations - You can combine static product information from a record with live data such as current inventory levels, pricing updates, customer ratings, and shipping costs pulled directly from your backend or e-commerce platform. You also add personalized product suggestions based on what each customer has recently viewed. This way, the product details you show are always accurate and tailored for each shopper in real time.
- Customer experience platforms - You can merge personalized data created inside Synerise — like recent product views or preferences—with up-to-date information about the customer’s account or status pulled from your external CRM or other backend systems. For example, you could show each customer their current membership level or available offers alongside personalized clothing recommendations, all combined into one seamless experience.
- Legacy CMS modernization - If you’re still using an older CMS for your website content, you can fetch static content (like text and images) from your legacy CMS, then enrich it by adding AI-driven Synerise product recommendations, personalized promotions, and personalized messages without needing to move your content elsewhere.
Procedure
-
Go to
 Data Modeling Hub > External sources > New external.
Data Modeling Hub > External sources > New external.
Result: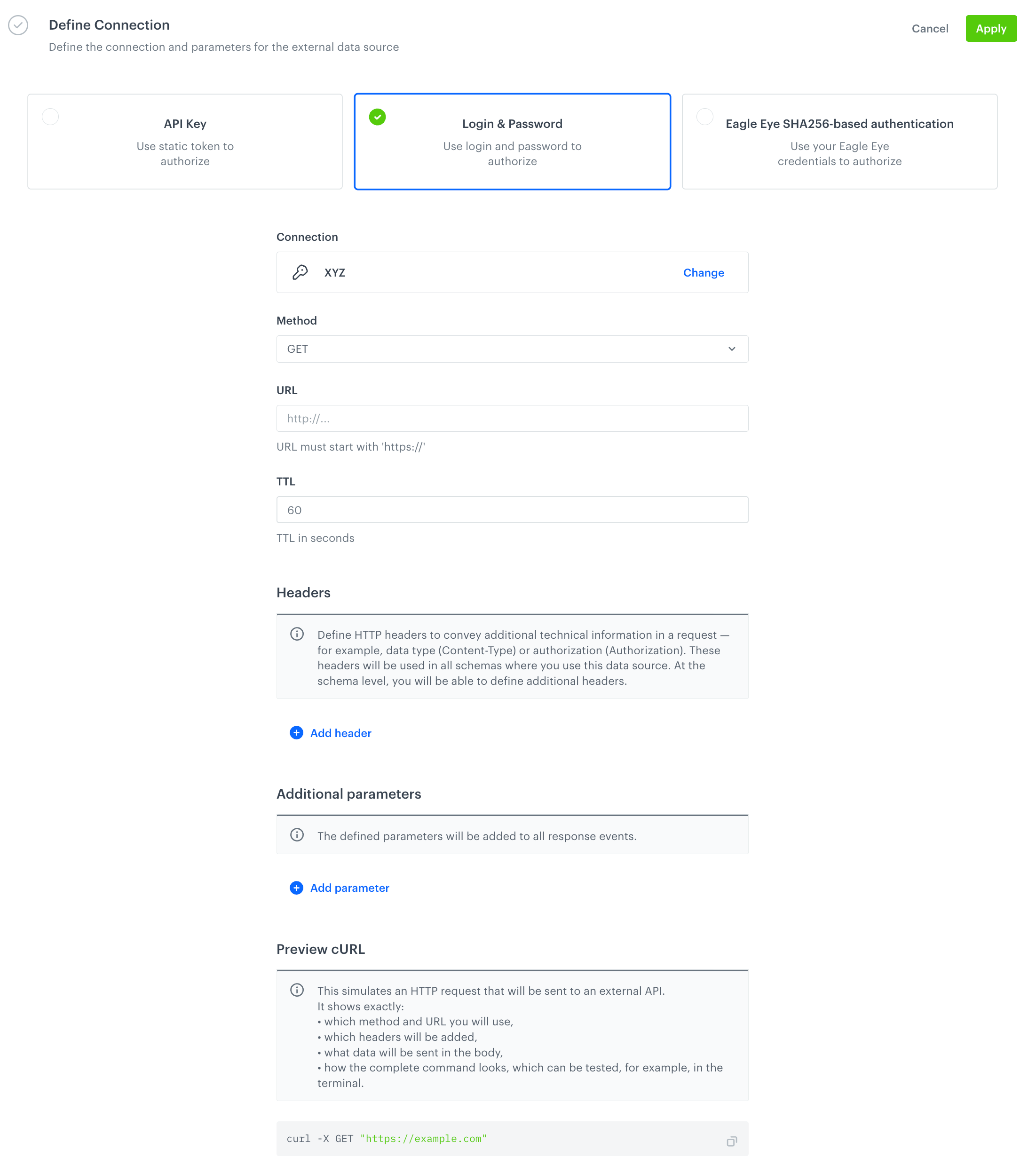
An empty configuration form of an external source -
Select the method of authorization to the external source to which you will make a request.
-
API Key - This method lets you authenticate using an API secret by including it in a header of your choice or in a URL parameter — example outputs:
- the authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer [secret] - URL parameter:
client_id=[rendered secret].
When you use this connection, the token will be automatically added to either the request header or the request URL with every request.
Click here to see the instructions- Click Select connection.
- If the connection you want to use is in the list, select it and proceed to selecting the HTTP method.
- If the connection list is empty or you don’t see a connection, you must:
- At the bottom of the dropdown list, click Add connection.
- In the Connection name field, enter the name of your connection (it’s visible only on the Select connection dropdown list).
- In the Secret field, enter an API Key.
- If you:
- specify the value in the Headers section, the API key will be added as a header to the request. For example,
x-api-key: {{secret}}where{{secret}}retrieves the value of the Secret field to anonymize the API key value. - provide the value in the URL Parameters section, the API key will be appended to the request’s URL as a parameter.
- specify the value in the Headers section, the API key will be added as a header to the request. For example,
- Click Create.
The connection you created can be used later in external sources.
- If the connection list is empty or you don’t see a connection, you must:
- the authorization header:
-
Login & Password - This method lets you use basic authentication to authenticate with the remote server.
Click here to see the instructions- Click Select connection.
- In the connection list:
- If the connection you want to use is in the list, select it and proceed to selecting the HTTP method.
- If the connection list is empty or you don’t see a connection, you must:
- At the bottom of the dropdown list, click Add connection.
- In the Connection name field, enter the name of your connection (it’s visible only on the Select connection dropdown list).
- In the Login field, enter a login.
- In the Password field, enter the password.
- Click Create.
The connection you created can be used later in external sources.
-
SHA256-based authentication - This method is recommended exclusively for connecting with Eagle Eye. This method lets you authenticate using the SHA256 algorithm. When a target request is sent, the following headers are added to the request:
- X-EES-AUTH-CLIENT-ID – the value is taken from the Client ID field.
- X-EES-AUTH-HASH – the value is generated by concatenating the endpoint URI, request body, and client secret, and then hashing the result using SHA256.
Click here to see the instructions- Click Select connection.
- In the connection list:
- If the connection you want to use is in the list, select it and proceed to selecting the HTTP method.
- If the connection list is empty or you don’t see a connection, you must:
- In the Connection name field, enter the name of the connection.
It’s used to find the connection on the list. - In Client ID, enter a unique identifier assigned to your application by the service provider.
- In Client secret, enter the client secret assigned to your application by the service provider.
- Confirm by clicking Create.
- In the Connection name field, enter the name of the connection.
-
-
From the Method dropdown list, select the request method to specify how the request will be sent.
-
In URL, provide the endpoint address to which the request will be made. You can include query parameters directly in the URL, for example:
https://example.com/products?productId={{profile.id}}&lang={{profile.language}}. Values of query parameters can use Jinjava, which allows you to dynamically pass profile data or record field values in the request. If the same parameter is defined both in the URL query string and in the Additional parameters section, the value from Additional parameters overrides the value from the URL. Because of this, parameters defined in the URL do not need to be repeated in Additional parameters unless you want to overwrite them. -
In TTL, specify how long the cached response from the external request will be valid. After changing data, the old value can be visible through brickworks for a maximum time defined here. You can set maximum 1800s value.
We recommend setting short TTL for fast-changing data and longer for stable information. -
In the Headers section, by clicking Add header, you can define the request headers such as
content-type: application/jsonin the key-value form: in the left field (key) provide a header name, in the right field, provide a value.
These headers will be used in all schemas where you use this data source. -
If you selected the POST method, you must provide the request body in the Body section.
- Optionally, by clicking
 , you can use a snippet which will let you add dynamic values to the request body.
, you can use a snippet which will let you add dynamic values to the request body. - If you used snippets, enable processing of the Jinjava template by selecting the fields in a request that contain them in the Treat the body selected parameters as Jinjava section.
- You can use the following options:
- From the Cast to dropdown list, select the data type to cast the Jinjava result to
- Use the Strict toggle to define what happens when casting is not successful:
- when the option is disabled, sets Jinjava to a null value,
- when the option is enabled, returns an error in generating an object from a record
The indicated parameter will be rendered as Jinjava by the backend and you can define the value type returned.
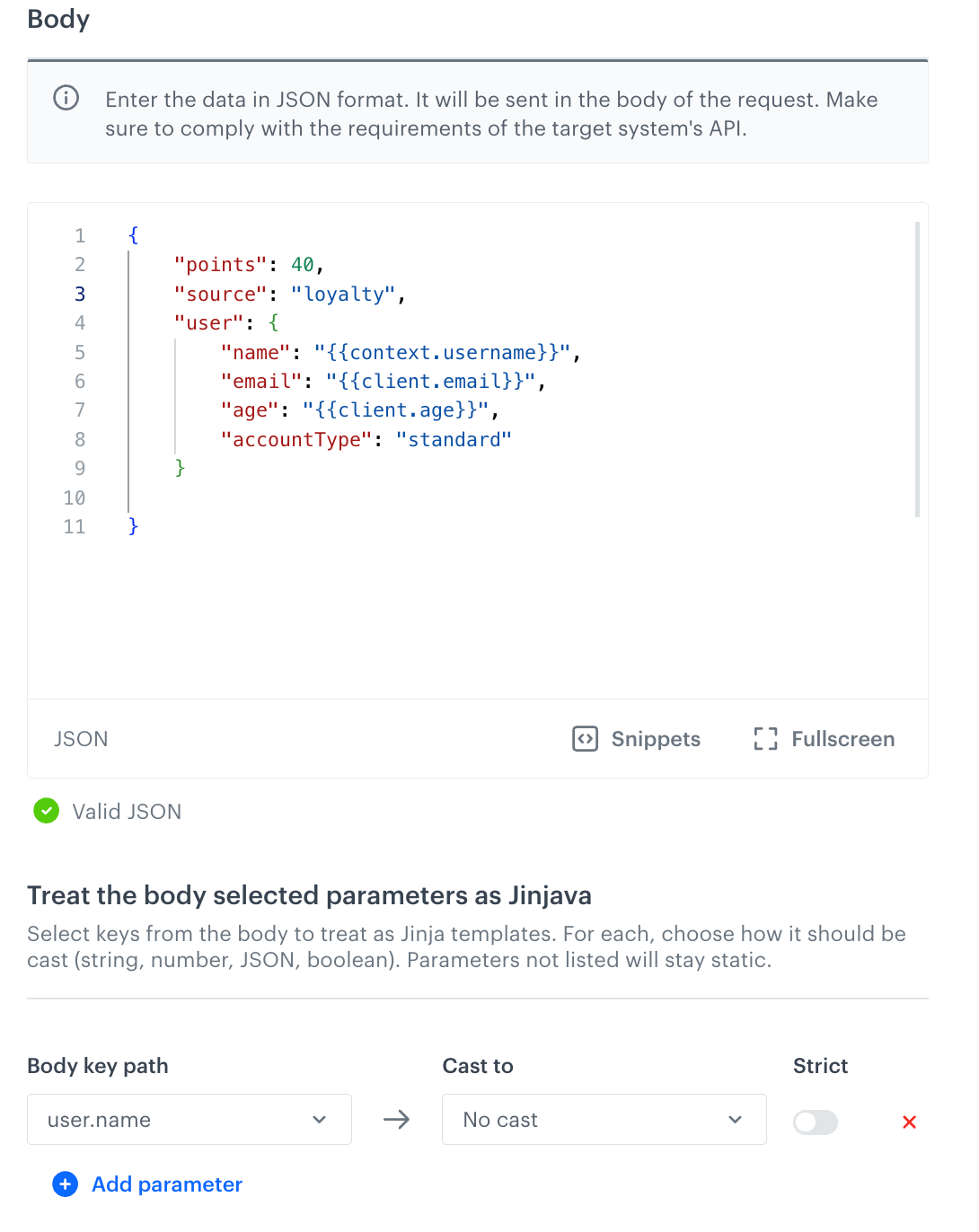
Example body with dynamic values
- Optionally, by clicking
-
In the Additional parameters section, by clicking Add parameter, you can add custom parameters to the events generated by the response from the external source. In the left field (key) provide a parameter name; in the right field, provide its value.
- You can use this, for example, to create a common parameter for events from a particular external source.
- The parameters will be added to
brickworks.generatedand/orbrickworks.generated.errorevents.
Testing the external source
In the Preview cURL section, you can view the cURL request that will be sent to the endpoint when invoking the object with the record result or previewing a record that references an external source.
You can copy this cURL command and run it in your terminal or use it with any API testing tool to see how the request works.
Using external sources in a record
See the External Data section.